Mobility plays a crucial role in our daily lives. It influences how we commute to work, transport goods, and spend our leisure time. Given the challenges of climate change and traffic congestion, the transition in transportation is becoming increasingly urgent. The goal is to achieve sustainable, efficient, and secure mobility. And this is where data comes into play. Data will become more relevant in shaping the transportation transition. The same applies to data spaces and platforms. Only by sharing data can it be utilized to its fullest potential. How do market participants and users of mobility, in general, and railways, in particular, benefit from data spaces and data sharing communities like the Mobility Data Space?
Intelligent Transportation Systems for Seamless Journeys: The Role of the EU Directive
The transition in transportation is a complex goal that requires a shift towards more sustainable modes of transport and systems. Data plays a central role as it forms the basis for innovations and changes.
Since 2019, transport authorities, transport and infrastructure operators, as well as providers of demand-driven transport services, are obligated to share their travel and traffic data. This is facilitated through National Access Points (NAP). In Germany, for example, this is the Mobility Hub of the Federal Ministry of Digital and Transport (BMDV), which has replaced the previous Mobility Data Marketplace (MDM). An overview of the NAPs in other countries can be found here.
These obligations are based on regulations stemming from the European Directive on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS). They stipulate that individuals should have access to multimodal information about their trips when planning and during their journeys within the EU.
From obligation to opportunity: From NAP to Data Space
Of the nearly 13,500 data packages (as of October 2023) on the German NAP, the Mobility Hub, the vast majority are open data that can be used without a license. They are primarily published on a legal basis.
However, additional data come into play when developing comprehensive new mobility services. Many of them find their way onto the Mobility Data Space (MDS) and can be traded from there while respecting ownership rights.
The MDS is considered a flagship project of the European cloud initiative Gaia-X and serves as a model for the development of further data spaces. The non-profit organization DRM Datenraum Mobilität GmbH, which emerged from a project of the acatech Foundation, is the carrier; the MDS is funded by the Federal Ministry of Digital and Transport (BMDV).
Karl-Heinz Streibich is the President of acatech – Deutsche Akademie der Technikwissenschaften, which is significantly involved in the development of the MDS. He states: “Relevant data and its utilization unlock a key resource of our time. This particularly applies to mobility. The sovereign exchange of relevant data is of central importance for our society.” He emphasizes the broad range of data that sets the MDS apart from other platforms: “The Mobility Data Space enables everyone who wants to shape the mobility of the future to equally, transparently, and autonomously exchange a wide range of mobility data: from current weather conditions to information about construction sites and air quality.”

In his speech at Charles University on August 29, 2022 in Prague, German Chancellor Olaf Scholz emphasized the importance of a unified, cross-border space for mobility data. He highlighted that Germany has taken the lead with the Mobility Data Space and called for it to be connected with the rest of Europe. His appeal was for everyone who wants to make a difference to join in, so that together, we can become pioneers worldwide.
Increased Flexibility and Convenience: Benefits for Users When Using Different Modes of Transportation
What do users gain from this data exchange? A lot. Let’s consider this practical example:
When not driving in their own car – which should be the goal – people rarely use just one mode of transportation.
To get to the train station or to move around at the destination, additional options come into play, such as taxis, car sharing, e-scooters, or rental bicycles, in addition to public transport. Due to the exchange of data between transportation providers regarding schedules and locations, coordinating these options has become much easier.
Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS) apps connect different modes of transportation on a single platform, going beyond traditional public transport apps. Even if travel plans change, for example, due to delays, new connections and possibilities can be found quickly – regardless of the mode of transportation.
One such app is the mobility platform Jelbi by the Berlin public transport company Berliner Verkehrsbetriebe, which was voted the best mobility app in Germany in 2023. With just one registration, users can book and use around 70,000 vehicles, including buses, trains, rental bikes, e-mopeds, e-scooters, rental cars, and taxis.
The Mobility Data Space: How Data can Improve Mobility Even Further
The data in the Mobility Data Space then takes things a step further.
The multimodal mobility platform FREE NOW combines data from transportation providers with weather data from the German Weather Service (DWD). Users can make real-time decisions on which mode of transportation is most suitable based on weather forecasts and book it directly. For example, on a sunny day, an e-scooter might be the best choice, while during heavy rain, a taxi would be more appropriate.
Explore more business cases on the Mobility Data Space website.
The Innovation Potential of Data Spaces in the Mobility Industry
The aforementioned business cases are just the beginning. The innovation potential through data in the mobility industry is enormous. Marketplaces like MDS foster collaboration among various stakeholders in the mobility sector. Companies can access a wide range of data to develop sustainable, efficient, and secure mobility solutions, thereby driving a transformation of the transportation sector.
In these areas, the innovation potential through data is particularly high:
Efficient traffic management
Data on traffic flows, congestion, and road usage enable more accurate traffic planning and control. This leads to smoother traffic and reduced traffic congestion.
Efficient traffic management
Data enables monitoring and reduction of the CO2 footprint in the transportation sector. This is crucial in combating climate change.
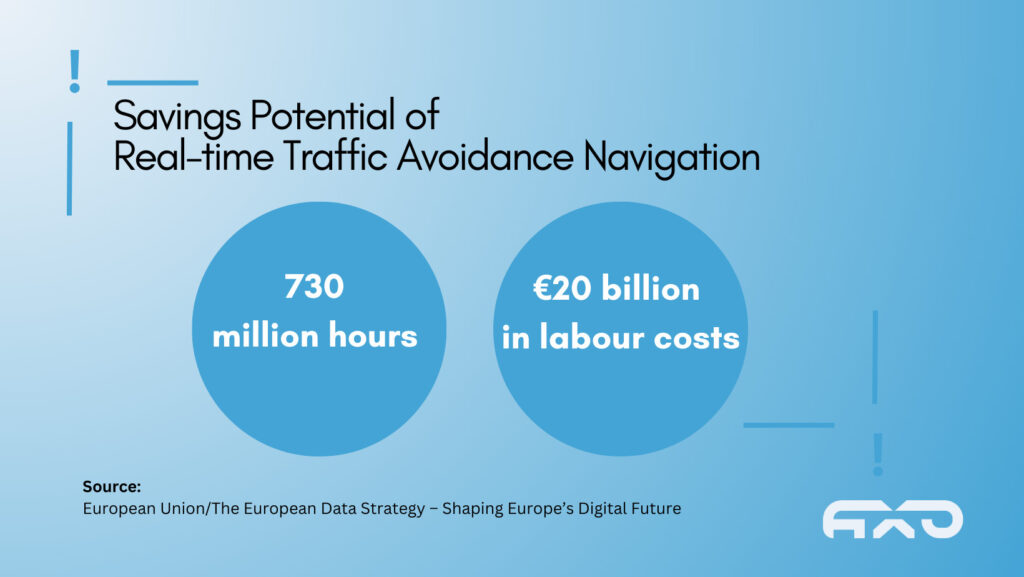
Traffic safety
Data-driven technologies such as autonomous driving and driver assistance systems, as well as collision avoidance systems, contribute to improving traffic safety. Accidents can be reduced and lives can be saved.
Customer-oriented services
By analyzing data on consumer behavior and needs, customized services and solutions can be developed to enhance customer satisfaction.
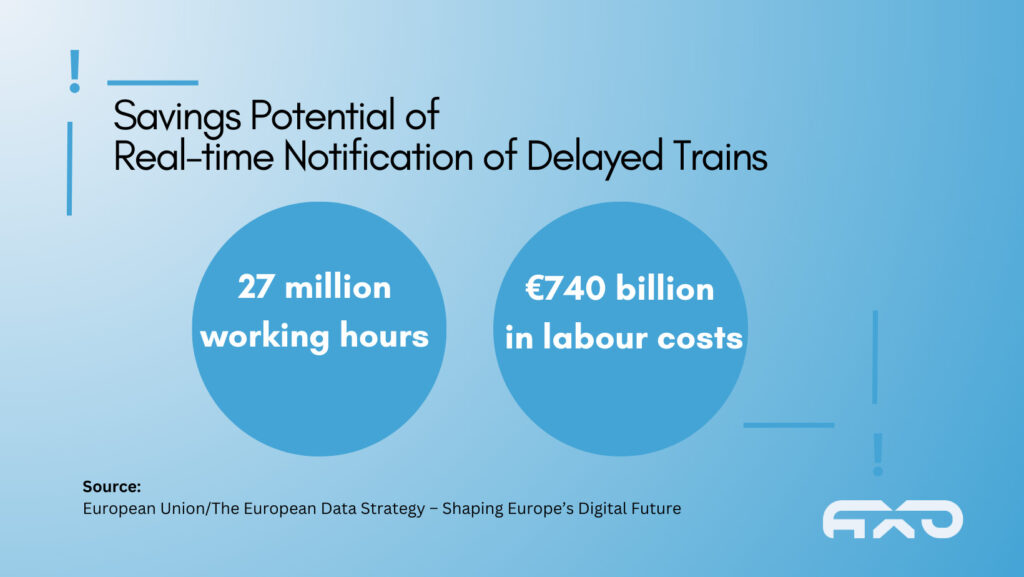
Innovation in the railway industry
Specifically in the railway industry, data provides opportunities for improving operations, maintenance, and intermodality. Railway companies can offer more punctual trains, enhance safety, and promote more environmentally friendly solutions.
Transport planning and management
Data support cities and municipalities in the planning of transportation infrastructure and policies. They enable the identification of bottlenecks and the implementation of effective measures to improve traffic.
Transportation logistics and freight transport
In freight transportation, data allows for better logistics and route optimization. This reduces fuel consumption and lowers costs.
Decentralized Data Exchange on the Data Space: Protecting Data Sovereignty
Data privacy is a sensitive issue. The International Data Spaces solve this conflict of goals through their unique architectural concept. The MDS is based on a decentralized, GDPR-compliant approach that enables data exchange directly between partners. Owners retain data sovereignty at all times.
The MDS itself does not store any external raw data, but only provides a data catalog for searching for data offerings and an infrastructure for decentralized data exchange. Participants also coordinate the purpose and price among themselves. To simplify contract negotiations, the MDS provides sample clauses.
If partners agree about the conditions, they exchange the data directly among each other via a connector (EDC connector / industry standard or CaaS – Connector-as-a-Service). All participants are authenticated using a secure procedure.
The technical process, for example, is explained on the pages of the Fraunhofer Institute.

Sustainable Mobility through the Use of Data: The Path to the Transportation Transition
The current challenges in the transportation sector can be successfully overcome by utilizing data. It is essential in creating a sustainable and efficient mobility system.
Data is the key to achieving a successful transportation transition, as it enables us to make mobility more efficient, sustainable, and safe. Data marketplaces foster collaboration and innovation in the mobility industry.
For railways and rail infrastructure, data and data platforms offer specific opportunities to optimize rail transportation and make it more environmentally friendly.
The future of mobility lies in the hands of those who seize the opportunities presented by data and data marketplaces to drive the transportation transition. Let’s seize these opportunities!


